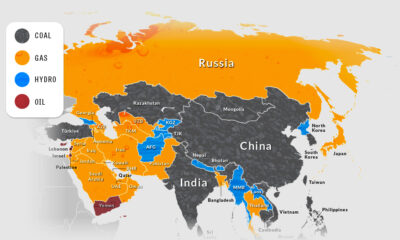
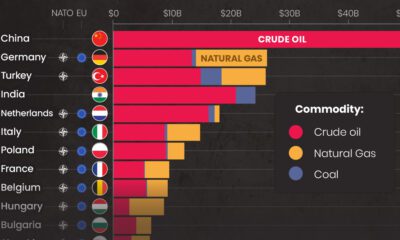
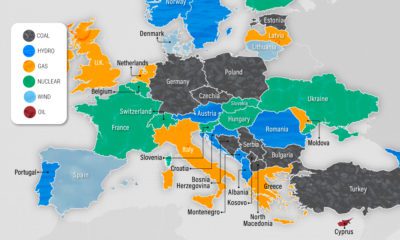
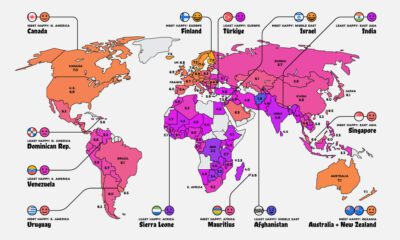
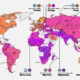
With energy consumption vital for life and business, governments often look to fossil fuel subsidies to make energy as affordable as possible. These subsidies artificially reduce the price of fossil fuels and generally take two forms:
Production subsidies occur when governments provide tax cuts or direct payments that reduce the cost of producing coal, oil, or gas. Consumption subsidies cut fuel prices for the end-user through price controls and other such measures.
Each year, governments around the world pour nearly half a trillion dollars into fossil fuel subsidies. This chart breaks down a decade of fossil fuel consumption subsidies by energy source using data from the International Energy Agency (IEA).
Breaking Down Fossil Fuel Consumption Subsidies
Since 2010, governments have spent over $5 trillion in fossil fuel consumption subsidies. The majority of this sum went towards making oil more affordable, as seen below: Fossil fuel subsidies fell to a decade low in 2020 as the pandemic hampered fuel consumption and triggered a nosedive in oil prices. However, after two years of straight declines, the IEA estimates that governments around the world spent $440 billion on subsidizing fossil fuel consumption over 2021, representing a 142% rise year-over-year. Breaking down the subsidies by fuel, oil accounts for 43% or over $2 trillion of all subsidies between 2010 and 2020. Together, oil and electricity generated by fossil fuels received nearly 75% of all subsidies. Despite growing support for the clean energy transition, the fossil fuel industry reaps the benefits of billions in subsidies annually—but why?
Why Do Governments Subsidize Fossil Fuels?
High energy prices can have rippling effects throughout an economy. For consumers, heating and transportation become more expensive. And for producers who use energy and oil as inputs, the cost of goods and services goes up. Often, governments turn to energy subsidies to keep prices down and encourage economic activity. Therefore, there’s a high cost to removing these subsidies, especially in developing countries where large parts of the population might lack access to affordable energy. But fossil fuel subsidies can also have detrimental effects. By artificially lowering prices, they can encourage overconsumption of carbon-intense fuels, creating negative externalities through adverse environmental and health impacts. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency, these add up to an amount anywhere between $2.6 to $8.1 trillion globally. Despite these disadvantages, fossil fuels remain an important part of the global energy mix, with continued support from governments. And with energy prices soaring, 2022 could be another year of billions in fossil fuel subsidies. on
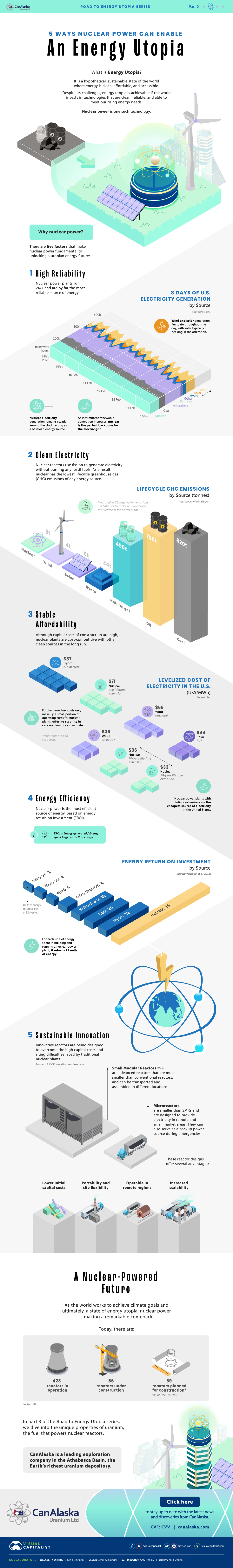
#1: High Reliability
Nuclear power plants run 24/7 and are the most reliable source of sustainable energy. Nuclear electricity generation remains steady around the clock throughout the day, week, and year. Meanwhile, daily solar generation peaks in the afternoon when electricity demand is usually lower, and wind generation depends on wind speeds.As the use of variable solar and wind power increases globally, nuclear offers a stable and reliable backbone for a clean electricity grid.
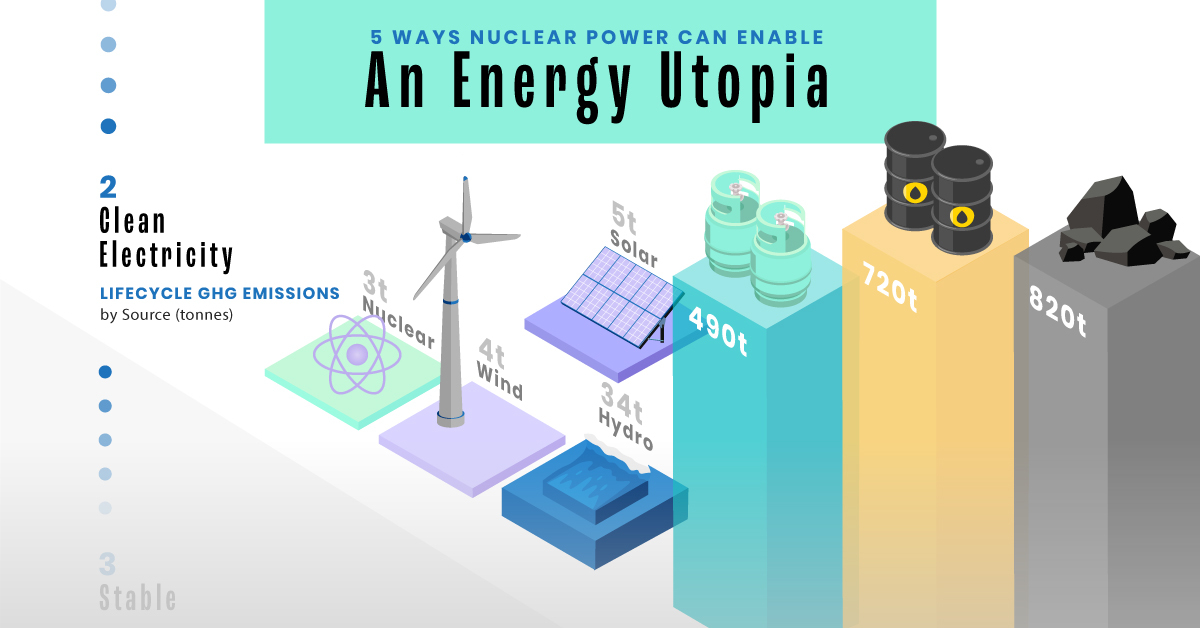
#2: Clean Electricity
Nuclear reactors use fission to generate electricity without any greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.Consequently, nuclear power is the cleanest energy source on a lifecycle basis, measured in CO2-equivalent emissions per gigawatt-hour (GWh) of electricity produced by a power plant over its lifetime. The lifecycle emissions from a typical nuclear power plant are 273 times lower than coal and 163 times lower than natural gas. Furthermore, nuclear is relatively less resource-intensive, allowing for lower supply chain emissions than wind and solar plants.
#3: Stable Affordability
Although nuclear plants can be expensive to build, they are cost-competitive in the long run. Most nuclear plants have an initial lifetime of around 40 years, after which they can continue operating with approved lifetime extensions. Nuclear plants with lifetime extensions are the cheapest sources of electricity in the United States, and 88 of the country’s 92 reactors have received approvals for 20-year extensions. Additionally, according to the World Nuclear Association, nuclear plants are relatively less susceptible to fuel price volatility than natural gas plants, allowing for stable costs of electricity generation.
#4: Energy Efficiency
Nuclear’s high energy return on investment (EROI) exemplifies its exceptional efficiency. EROI measures how many units of energy are returned for every unit invested in building and running a power plant, over its lifetime. According to a 2018 study by Weissbach et al., nuclear’s EROI is 75 units, making it the most efficient energy source by some distance, with hydropower ranking second at 35 units.
#5: Sustainable Innovation
New, advanced reactor designs are bypassing many of the difficulties faced by traditional nuclear plants, making nuclear power more accessible.
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) are much smaller than conventional reactors and are modular—meaning that their components can be transported and assembled in different locations. Microreactors are smaller than SMRs and are designed to provide electricity in remote and small market areas. They can also serve as backup power sources during emergencies.
These reactor designs offer several advantages, including lower initial capital costs, portability, and increased scalability.
A Nuclear-Powered Future
Nuclear power is making a remarkable comeback as countries work to achieve climate goals and ultimately, a state of energy utopia. Besides the 423 reactors in operation worldwide, another 56 reactors are under construction, and at least 69 more are planned for construction. Some nations, like Japan, have also reversed their attitudes toward nuclear power, embracing it as a clean and reliable energy source for the future. CanAlaska is a leading exploration company in the Athabasca Basin, the Earth’s richest uranium depository. Click here to learn more now. In part 3 of the Road to Energy Utopia series, we explore the unique properties of uranium, the fuel that powers nuclear reactors.