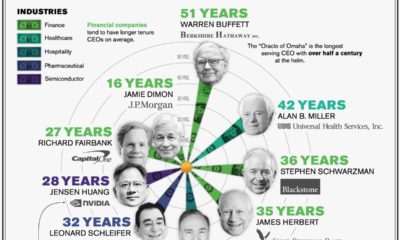
This graphic provides context into the consumer debt situation using data from the end of 2021.
Housing Vs. Non-Housing Debt
The following table includes the data used in the above graphic. Housing debt covers mortgages, while non-housing debt covers auto loans, student loans, and credit card balances. Source: Federal Reserve
Trends in Housing Debt
Home prices have experienced upward pressure since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic. This is evidenced by the Case-Shiller U.S. National Home Price Index, which has increased by 34% since the start of the pandemic. Driving this growth are various pandemic-related impacts. For example, the cost of materials such as lumber have seen enormous spikes. We’ve covered this story in a previous graphic, which showed how many homes could be built with $50,000 worth of lumber. In most cases, these higher costs are passed on to the consumer. Another key factor here is mortgage rates, which fell to all-time lows in 2020. When rates are low, consumers are able to borrow in larger quantities. This increases the demand for homes, which in turn inflates prices. Ultimately, higher home prices translate to more mortgage debt being incurred by families.
No Need to Worry, Though
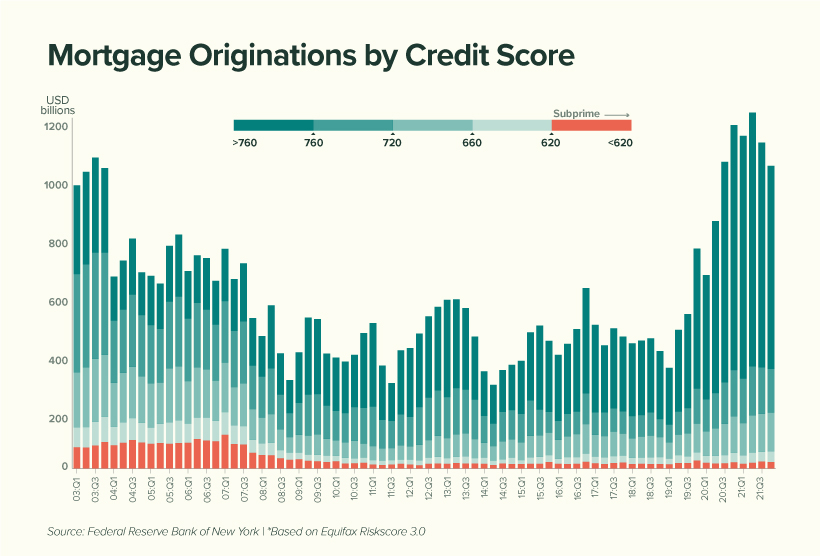
Economists believe that today’s housing debt isn’t a cause for concern. This is because the quality of borrowers is much stronger than it was between 2003 and 2007, in the years leading up to the financial crisis and subsequent housing crash. In the chart below, subprime borrowers (those with a credit score of 620 and below) are represented by the red-shaded bars:
We can see that subprime borrowers represent very little (2%) of today’s total originations compared to the period between 2003 to 2007 (12%). This suggests that American homeowners are, on average, less likely to default on their mortgage. Economists have also noted a decline in the household debt service ratio, which measures the percentage of disposable income that goes towards a mortgage. This is shown in the table below, along with the average 30-year fixed mortgage rate. Source: Federal Reserve While it’s true that Americans are less burdened by their mortgages, we must acknowledge the decrease in mortgage rates that took place over the same period. With the Fed now increasing rates to calm inflation, Americans could see their mortgages begin to eat up a larger chunk of their paycheck. In fact, mortgage rates have already risen for seven consecutive weeks.
Trends in Non-Housing Consumer Debt
The key stories in non-housing consumer debt are student loans and auto loans. The former category of debt has grown substantially over the past two decades, with growth tapering off during the pandemic. This can be attributed to COVID relief measures which have temporarily lowered the interest rate on direct federal student loans to 0%. Additionally, these loans were placed into forbearance, meaning 37 million borrowers have not been required to make payments. As of April 2022, the value of these waived payments has reached $195 billion. Over the course of the pandemic, very few direct federal borrowers have made voluntary payments to reduce their loan principal. When payments eventually resume, and the 0% interest rate is reverted, economists believe that delinquencies could rise significantly. Auto loans, on the other hand, are following a similar trajectory as mortgages. Both new and used car prices have risen due to the global chip shortage, which is hampering production across the entire industry. To put this in numbers, the average price of a new car has climbed from $35,600 in 2019, to over $47,000 today. Over a similar timeframe, the average price of a used car has grown from $19,800, to over $28,000. on A lagging stock market dented these fortunes against high interest rates, energy shocks, and economic uncertainty. But some of the world’s billionaires have flourished in this environment, posting sky-high revenues in spite of inflationary pressures. With data from Forbes Real-Time Billionaires List, we feature a snapshot of the richest people in the world in 2023.
Luxury Mogul Takes Top Spot
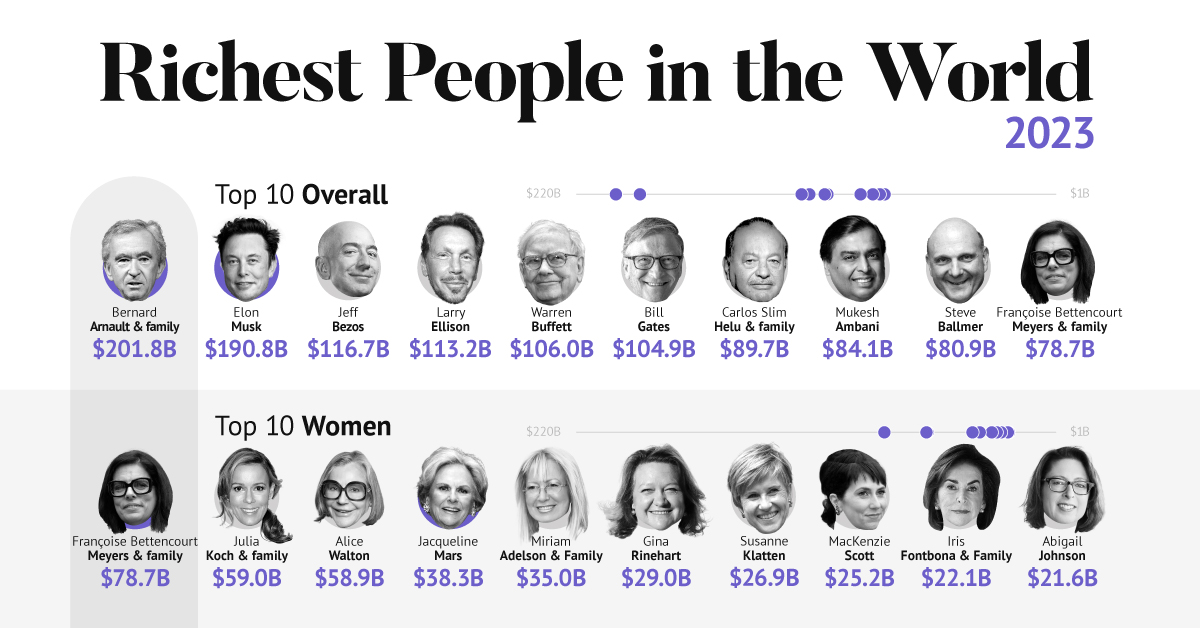
The world’s richest person is France’s Bernard Arnault, the chief executive of LVMH.
With 75 brands, the luxury conglomerate owns Louis Vuitton, Christian Dior, and Tiffany. LVMH traces back to 1985, when Arnault cut his first major deal with the company by acquiring Christian Dior, a firm that was struggling with bankruptcy.
Fast-forward to today, and the company is seeing record profits despite challenging market conditions. Louis Vuitton, for instance, has doubled its sales in four years.
In the table below, we show the world’s 10 richest people with data as of February 27, 2023:
Elon Musk, the second-wealthiest person in the world has a net worth of $191 billion. In October, Musk took over Twitter in a $44 billion dollar deal, which has drawn criticism from investors. Many say it’s a distraction from Musk’s work with Tesla.
While Tesla shares have rebounded—after falling roughly 70% in 2022—Musk’s wealth still sits about 13% lower than in March of last year.
Third on the list is Jeff Bezos, followed by Larry Ellison. The latter of the two, who founded Oracle, owns 98% of the Hawaiian island of Lanai which he bought in 2012 for $300 million.
Fifth on the list is Warren Buffett. In his annual letter to shareholders, he discussed how Berkshire Hathaway reported record operating profits despite economic headwinds. The company outperformed the S&P 500 Index by about 22% in 2022.
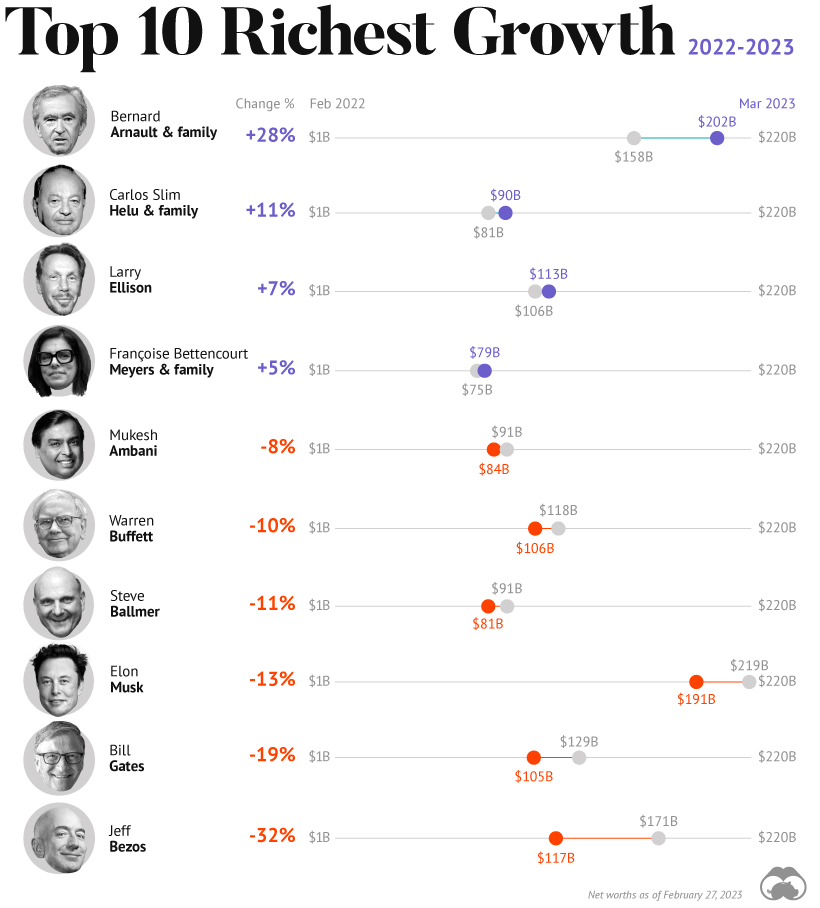
How Fortunes Have Changed
Given multiple economic crosscurrents, billionaire wealth has diverged over the last year. Since March 2022, just four of the top 10 richest in the world have seen their wealth increase. Two of these are European magnates, while Carlos Slim Helu runs the largest telecom firm in Latin America. In fact, a decade ago Slim was the richest person on the planet. Overall, as the tech sector saw dismal returns over the year, the top 10 tech billionaires lost almost $500 billion in combined wealth.
Recent Shakeups in Asia
Perhaps the most striking news for the world’s richest centers around Gautam Adani, formerly the richest person in Asia. In January, Hindenburg Research, a short-selling firm, released a report claiming that the Adani Group engaged in stock manipulation and fraud. Specifically, the alleged the firm used offshore accounts to launder money, artificially boost share prices, and hide losses. The Adani Group, which owns India’s largest ports—along with ports in Australia, Sri Lanka, and Israel—lost $100 billion in value in the span of a few weeks. Interestingly, very few Indian mutual funds hold significant shares in Adani Group, signaling a lack of confidence across India’s market, which was also cited in Hindenburg’s report. As a result, Mukesh Ambani has climbed to Asia’s top spot, controlling a $84 billion empire that spans from oil and gas and renewable energy to telecom. His conglomerate, Reliance Industries is the largest company by market cap in India.