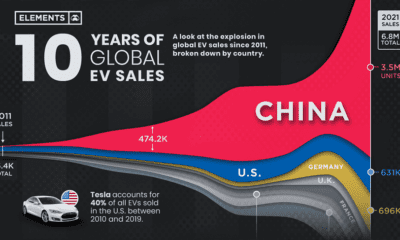
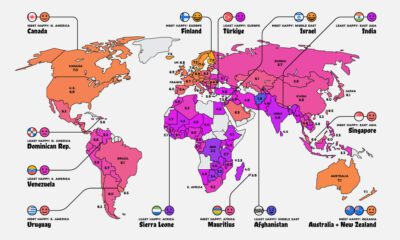
It’s the power of cobalt, along with several other energy metals, that keeps your lithium-ion battery running. The only problem? Getting the metal from the source to your electronics is not an easy feat, and this makes for an extremely precarious supply chain for manufacturers. Our infographic today comes to us from LiCo Energy Metals, and it focuses on where this important ingredient of green technology originates from, and the supply risks associated with its main sources.
What is Cobalt?
Cobalt is a transition metal found between iron and nickel on the periodic table. It has a high melting point (1493°C) and retains its strength to a high temperature. Similar to iron or nickel, cobalt is ferromagnetic. It can retain its magnetic properties to 1100°C, a higher temperature than any other material. Ferromagnetism is the strongest type of magneticism: it’s the only one that typically creates forces strong enough to be felt, and is responsible for the magnets encountered in everyday life. These unique properties make the metal perfect for two specialized high-tech purposes: superalloys and battery cathodes. Superalloys High-performance alloys drive 18% of cobalt demand. The metal’s ability to withstand intense temperatures and conditions makes it perfect for use in:
Turbine blades Jet engines Gas turbines Prosthetics Permanent magnets
Lithium-ion Batteries: Batteries drives 49% of demand – and most of this comes from cobalt’s usage in lithium-ion battery cathodes: The three most powerful cathode formulations for li-ion batteries all need cobalt. As a result, the metal is indispensable in many of today’s battery-powered devices.
Mobile phones (LCO) Tesla Model S (NCA) Tesla Powerwall (NMC) Chevy Volt (NMC/LMO)
The Tesla Powerwall 2 uses approximately 7kg, and a Tesla Model S (90 kWh) uses approximately 22.5kg of the energy metal.
The Cobalt Supply Chain
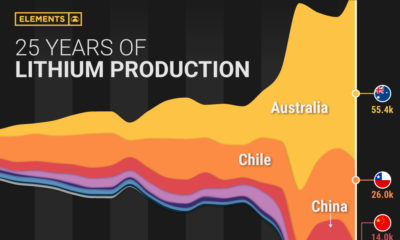
Cobalt production has gone almost straight up to meet demand, and production has more than doubled since the early 2000s. But while the metal is desired, getting it is the hard part:
- No native cobalt has ever been found in nature. There are four widely-distributed ores that exist, but almost no cobalt is mined from them as a primary source.
- Most cobalt production is mined as a by-product. This means it is hard to expand production when more is needed.
- Most production occurs in the DRC, a country with elevated supply risks:
The Future of Cobalt Supply
Companies like Tesla and Panasonic need reliable sources of the metal, and right now there aren’t many failsafes. The U.S. hasn’t mined cobalt in significant volumes since 1971, and the USGS reports that the United States only has 301 tonnes of the metal stored in stockpiles. The reality is that the DRC produces about half of all cobalt, and it also holds approximately 47% of all global reserves.
Why is this a concern for end-users?
- The DRC is one of the poorest, corrupt, and most coercive countries in the planet. It ranks:
151st out of 159 countries in the Human Freedom Index 176th out of 188 countries on the Human Development Index 178th out of 184 countries in terms of GDP per capita ($455) 148th out of 169 countries in the Corruption Perceptions Index
- The DRC has had more deaths from war since WWII than any other country on the planet. Recent wars in the DRC:
First Congo War (1996-1997) – A foreign invasion by Rwanda that overthrew the Mobutu regime. Second Congo War (1998-2003) – The bloodiest conflict in world history since WW2 with 5.4 million deaths.
- Human Rights in Mining The DRC government estimates that 20% of all cobalt production in the country comes from artisanal miners – independent workers who dig holes and mine ore without sophisticated mines or machinery. There are at least 100,000 artisanal cobalt miners in the DRC, and UNICEF estimates that up to 40,000 children could be in the trade. Children can be as young as seven years old, and they can work up to 12 hrs with physically demanding work, earning $2 per day. Meanwhile, Amnesty International alleges that Apple, Samsung, and Sony fail to do basic checks in making sure the metal in their supply chains did not come from child labor. Most major companies have vowed that any such practices will not be tolerated in their supply chains.
Other Sources
Where will tomorrow’s supply come from, and will the role of the DRC eventually diminish? Will Tesla achieve its goal of a North American supply chain for its key metal inputs? Mining exploration companies are already looking to regions like Ontario, Idaho, British Columbia, and the Northwest Territories to find tomorrow’s deposits: Ontario: Ontario is one of the only places in the world where cobalt-primary mines that have existed. This camp is nearby the aptly named town of Cobalt, Ontario, which is located halfway between Sudbury – the world’s “Nickel Capital”, and Val-d’Or, one of the most famous gold camps in the world. Idaho: Idaho is known as the “Gem State” while also being known for its silver camps in Couer D’Alene – but it has also been a cobalt producer in the past. BC: The mountains of British Columbia are known for their rich gold, silver, copper, zinc, and met coal deposits. But cobalt often occurs with copper, and some mines in BC have produced cobalt in the past. Northwest Territories: Cobalt can also be found up north, as the NWT becomes a more interesting mineral destination for companies. 160km from Yellowknife is a gold-cobalt-bismuth-copper deposit being developed. on
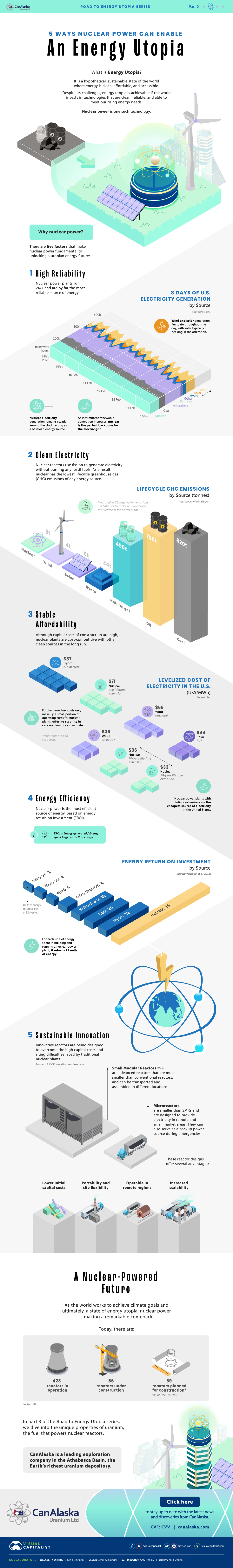
#1: High Reliability
Nuclear power plants run 24/7 and are the most reliable source of sustainable energy. Nuclear electricity generation remains steady around the clock throughout the day, week, and year. Meanwhile, daily solar generation peaks in the afternoon when electricity demand is usually lower, and wind generation depends on wind speeds.As the use of variable solar and wind power increases globally, nuclear offers a stable and reliable backbone for a clean electricity grid.
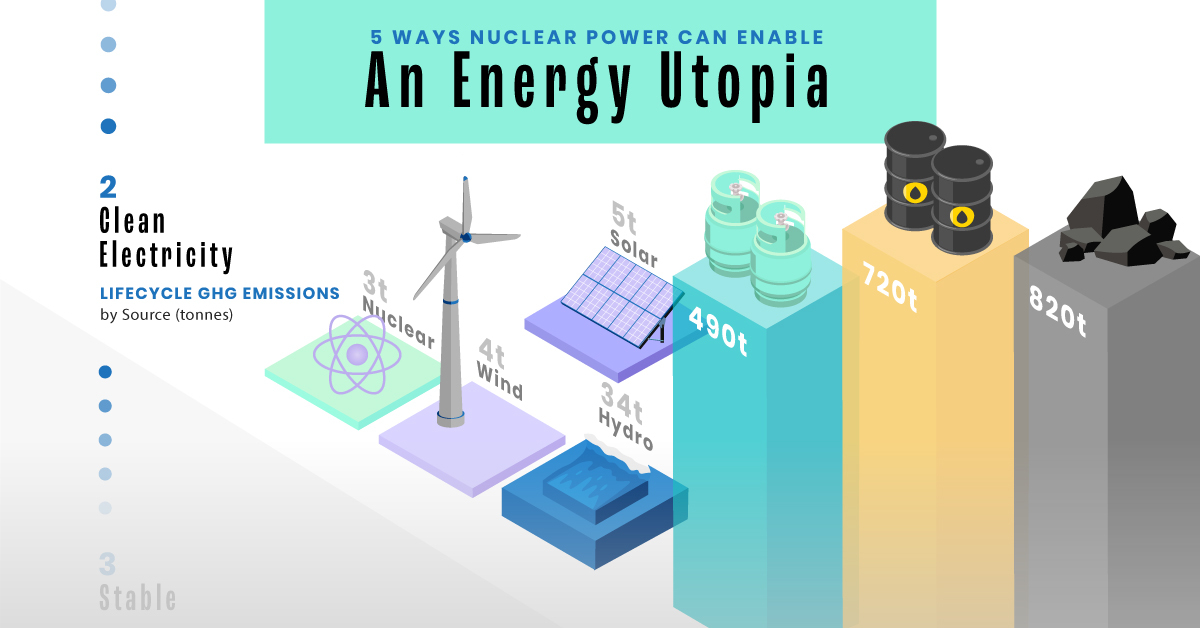
#2: Clean Electricity
Nuclear reactors use fission to generate electricity without any greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.Consequently, nuclear power is the cleanest energy source on a lifecycle basis, measured in CO2-equivalent emissions per gigawatt-hour (GWh) of electricity produced by a power plant over its lifetime. The lifecycle emissions from a typical nuclear power plant are 273 times lower than coal and 163 times lower than natural gas. Furthermore, nuclear is relatively less resource-intensive, allowing for lower supply chain emissions than wind and solar plants.
#3: Stable Affordability
Although nuclear plants can be expensive to build, they are cost-competitive in the long run. Most nuclear plants have an initial lifetime of around 40 years, after which they can continue operating with approved lifetime extensions. Nuclear plants with lifetime extensions are the cheapest sources of electricity in the United States, and 88 of the country’s 92 reactors have received approvals for 20-year extensions. Additionally, according to the World Nuclear Association, nuclear plants are relatively less susceptible to fuel price volatility than natural gas plants, allowing for stable costs of electricity generation.
#4: Energy Efficiency
Nuclear’s high energy return on investment (EROI) exemplifies its exceptional efficiency. EROI measures how many units of energy are returned for every unit invested in building and running a power plant, over its lifetime. According to a 2018 study by Weissbach et al., nuclear’s EROI is 75 units, making it the most efficient energy source by some distance, with hydropower ranking second at 35 units.
#5: Sustainable Innovation
New, advanced reactor designs are bypassing many of the difficulties faced by traditional nuclear plants, making nuclear power more accessible.
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) are much smaller than conventional reactors and are modular—meaning that their components can be transported and assembled in different locations. Microreactors are smaller than SMRs and are designed to provide electricity in remote and small market areas. They can also serve as backup power sources during emergencies.
These reactor designs offer several advantages, including lower initial capital costs, portability, and increased scalability.
A Nuclear-Powered Future
Nuclear power is making a remarkable comeback as countries work to achieve climate goals and ultimately, a state of energy utopia. Besides the 423 reactors in operation worldwide, another 56 reactors are under construction, and at least 69 more are planned for construction. Some nations, like Japan, have also reversed their attitudes toward nuclear power, embracing it as a clean and reliable energy source for the future. CanAlaska is a leading exploration company in the Athabasca Basin, the Earth’s richest uranium depository. Click here to learn more now. In part 3 of the Road to Energy Utopia series, we explore the unique properties of uranium, the fuel that powers nuclear reactors.