Today’s infographic from Pasha Brands dives into the huge consumer demand for craft products, and why investors should pay attention to this trend as it extends into cannabis.
The Perfect Craft Product
Chances are, you may have encountered any of the following at least once: microbrewed beer, specialty coffee, premium wine, or organic food. They’ve become so popular, that craft versions of all these are steadily carving a valuable niche in their original markets. Whether it’s introducing flavors into brews, slow-roasting beans, producing wine in small lots, or using a conscious “farm to table” label — what they have in common is the careful attention that’s paid to the process from start to end. Craft cannabis bears a strong resemblance to all of these in that way, as growing it involves extra care, compared to large-scale producers. For example, hand-trimming is more labor intensive than using machines, but results in products with superior quality. What are some other characteristics of craft cannabis?
Attention to detail A hands-on approach allows growers to personally ensure each cannabis plant is healthy. Sustainable practices The use of organic farming to save energy, creating a smaller environmental footprint. Social responsibility Smaller growers typically leverage local connections, creating employment opportunities. Artisanal branding Sophisticated and modern packaging helps appeal to different types of craft cannabis consumers.
It’s clear why consumers care about craft cannabis. But what does it offer investors?
Making the Case for Craft
Investors should be paying close attention to craft cannabis for three key reasons: a higher price point, a focus on quality, and access to the retail market.
Upscale Price Tag
On average, organic cannabis has a higher price point attached to it, compared to regular grade cannabis.
Industry average: $9.02/ gram Organic average: $11.40/ gram
Using organic methods to grow cannabis means that the final product on shelves boast an enhanced potency and effect. Since craft cannabis is also grown organically, it’s clear that consumers are willing to spend more to secure a premium product.
Promise of Quality
It might not come as a surprise that the most famous craft cannabis regions are also where the biggest volume of legal cannabis sales come from. California and Canada accounted for nearly 38% in global market share in 2017:
Worldwide sales: $9.5 billion California sales: $3 billion Rest of U.S. sales: $5.5 billion Canada sales: $0.6 billion Rest of world: $0.4 billion
These two areas have a foothold in cannabis sales, and with recreational legalization unfolding in both – and 75 million people living between the two jurisdictions – it will only continue to grow.
Opening the Doors
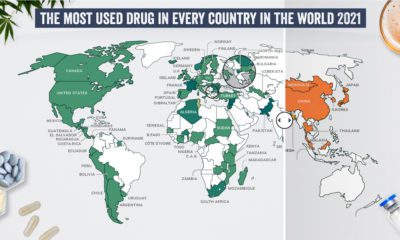
Following nation-wide legalization in Canada and an increasing number of states in the U.S., the continent is facing a cannabis shortage. Why? As it turns out, while craft growers are abundant, they still face regulatory hurdles in order to move from the “gray” underground market into launching legal operations. Craft cannabis could be a cornerstone for industry growth, but its growers have been in the shadows for a long time. As cannabis gains momentum, tapping into the huge network of craft growers will be key for success. on Humans have a storied and complicated relationship with drugs. Defined as chemical substances that cause a change in our physiology or psychology, many drugs are taken medicinally or accepted culturally, like caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol. But many drugs—including medicines and non-medicinal substances taken as drugs—are taken recreationally and can be abused. Each country and people have their own relationship to drugs, with some embracing the use of specific substances while others shun them outright. What are the most common drugs that are considered generally illicit in different parts of the world? Today’s graphics use data from the UN’s World Drug Report 2021 to highlight the most prevalent drug used in each country.
What Types of Common Drugs Are Tracked?
The World Drug Report looks explicitly at the supply and demand of the international illegal drug market, not including commonly legal substances like caffeine and alcohol. Drugs are grouped by class and type, with six main types of drugs found as the most prevalent drugs worldwide.
Cannabis*: Drugs derived from cannabis, including hemp. This category includes marijuana (dried flowers), hashish (resin), and other for various other parts of the plant or derived oils. Cocaine: Drugs derived from the leaves of coca plants. Labeled as either cocaine salts for powder form or crack for cocaine processed with baking soda and water into rock form. Opioids: Includes opiates which are derived directly from the opium poppy plant, including morphine, codeine, and heroin, as well as synthetic alkaloids. Amphetamine-type Stimulants (ATS): Amphetamine and drugs derived from amphetamine, including meth (also known as speed), MDMA, and ecstasy. Sedatives and Tranquilizers: Includes other drugs whose main purpose is to reduce energy, excitement, or anxiety, as well as drugs used primarily to initiate or help with sleep (also called hypnotics). Solvents and Inhalants: Gases or chemicals that can cause intoxication but are not intended to be drugs, including fuels, glues, and other industrial substances.
The report also tracked the prevalence of hallucinogens—psychoactive drugs which strongly affect the mind and cause a “trip”—but no hallucinogens ranked as the most prevalent drug in any one country. *Editor’s note: Recreational cannabis is legal in five countries, and some non-federal jurisdictions (i.e. states). However, in the context of this report, it was included because it is still widely illicit in most countries globally.
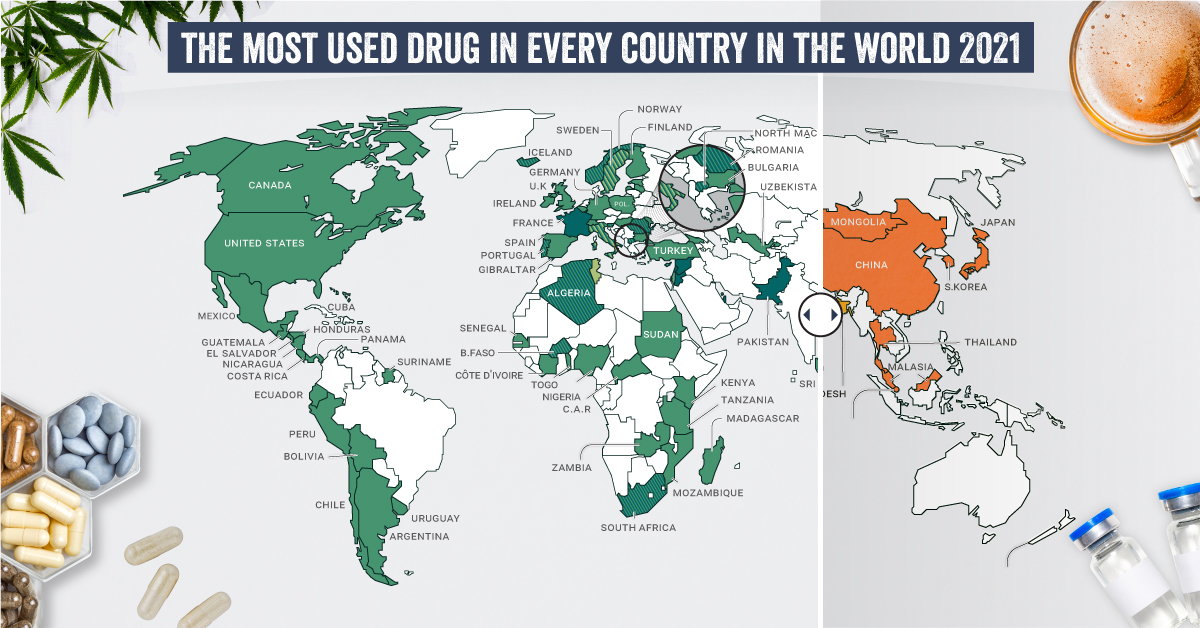
The Most Prevalent Drug in Each Country
According to the report, 275 million people used drugs worldwide in 2020. Between the ages of 15–64, around 5.5% of the global population used drugs at least once. Many countries grouped different types of the same drug class together, and a few like Saudi Arabia and North Macedonia had multiple different drug types listed as the most prevalent. But across the board, cannabis was the most commonly prevalent drug used in 107 listed countries and territories: How prevalent is cannabis worldwide? 72 locations or more than two-thirds of those reporting listed cannabis as the most prevalent drug. Unsurprisingly these include countries that have legalized recreational cannabis: Canada, Georgia, Mexico, South Africa, and Uruguay.
How Common Are Opioids and Other Drugs?
Though the global prevalence of cannabis is unsurprising, especially as it becomes legalized and accepted in more countries, other drugs also have strong footholds. Opioids (14 locations) were the most prevalent drugs in the Middle-East, South and Central Asia, including in India and Iran. Notably, Afghanistan is the world’s largest producer of opium, supplying more than 90% of illicit heroin globally. Amphetamine-type drugs (9 locations) were the third-most common drugs overall, mainly in East Asia. Methamphetamine was the reported most prevalent drug in China, South Korea, and Japan, while amphetamine was only the most common drug in Bangladesh. However, it’s important to note that illicit drug usage is tough to track. Asian countries where cannabis is less frequently found (or reported) might understate its usage. At the same time, the opioid epidemic in the U.S. and Canada reflects high opioid usage in the West. As some drugs become more widespread and others face a renewed “war,” the landscape is certain to shift over the next few years.