Visualizing the Footprint of Highways in American Cities
Driving on the open road is a defining feature of the American experience, made possible by coast-to-coast highways. It defined a generation of life and ingrained the automobile into the urban fabric of American cities, for better and worse. Today’s animations show how highways reshaped the downtown cores of six American cities and created new patterns of urban life. But first, some background information on the creation of the interstate system.
The Interstate Highway System
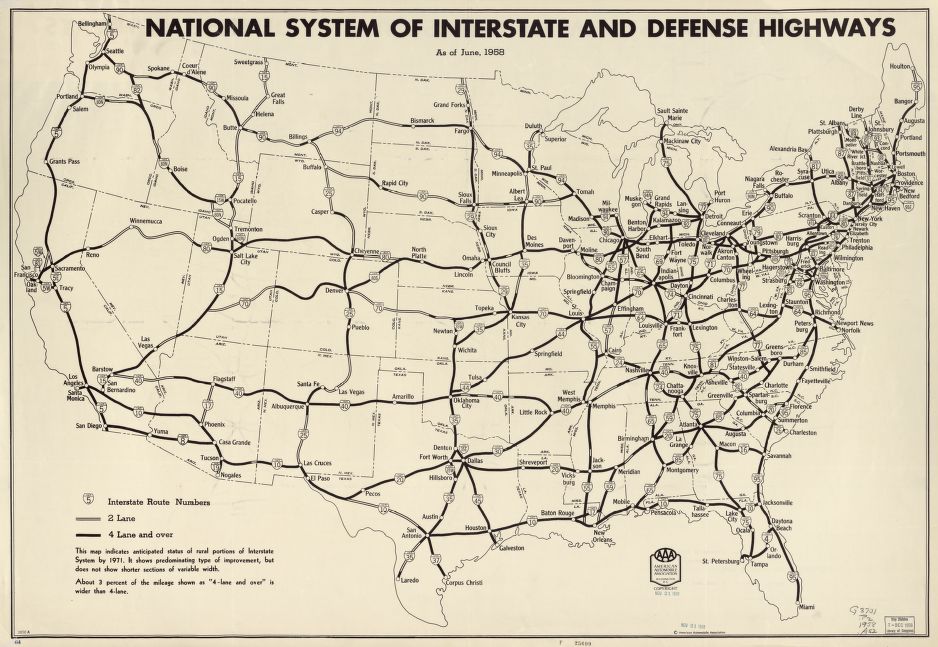
The U.S. Interstate System was created on June 29, 1956, when Dwight Eisenhower signed the Federal-Aid Highway Act. It would eventually run 46,876 miles, cost $521 billion and take 36 years to complete.
From San Diego to Bangor, the interstate highway system connected Americans and opened up the country to commerce and geographic mobility like never before, but for all its benefits, this new transportation network ripped through established patterns of urban and town life, creating a new era of urban development.
The Legacy of Highways: The Suburbs and Inner Cities
The vast geography of continental America helped to entrench personal mobility and freedom into American society. Highways and automobiles accelerated this lifestyle and even changed the shape of entire cities. According to Prof. Nathaniel Baum-Snow of the University of Toronto, between 1950 and 1990, the population of central cities in the U.S. declined by 17% despite a population growth of 72% in larger metropolitan areas during the same period. Baum-Snow posits that, had the interstate highway system not been built, central cities’ populations would have increased 8%. Firms followed the workers to the suburbs, but the highways system also created additional benefits for these firms. Cross-country road access freed manufacturing from ports and downtown rail hubs, while allowing economies to operate across larger distances, altering the dynamics of typical urban economies. Faced with this new reality, inner cities struggled in years to come.
Inner Cities
The introduction of highways created an increase in the supply of land for development through faster commutes to outlying areas. In 1950, half of all jobs were located in central cities. By 1990, less than one-third of urban jobs were located in the core of American cities. Benefits of new development accrued to the outer areas while the construction of the highways in inner cities displaced largely low-income communities, segregated neighborhoods, increased the amount of air and noise pollution, devalued surrounding properties, and removed access to jobs for those without a car, further concentrating poverty.
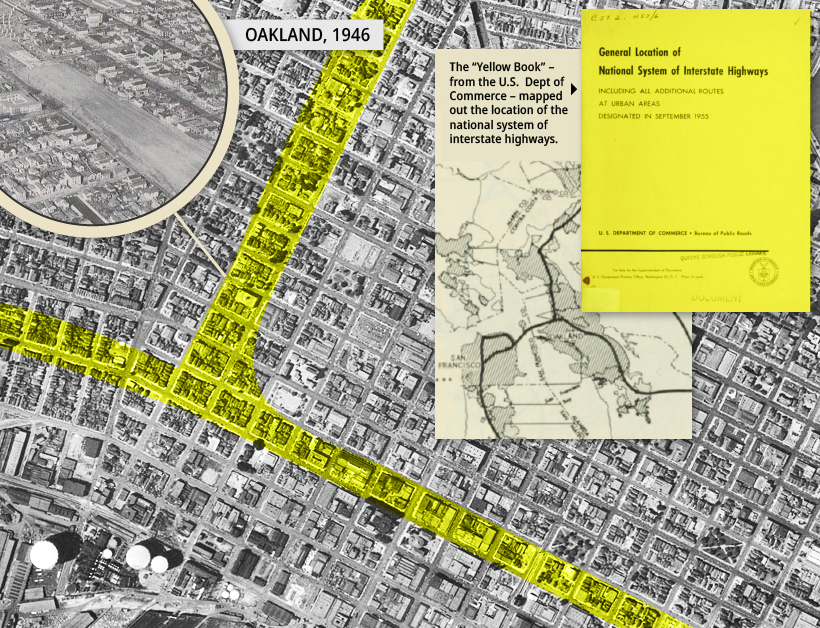
Before and After: Six American Cities
A bird’s eye view of six American cities reveals what was and what is now. By overlaying existing highways over the neighborhoods they replaced, it becomes clear how much interstate construction drastically altered America’s urban landscape. Public opposition to the construction of I-980 was so strong that developers abandoned the project in 1971, only to complete it over a decade later. The I-95 carved through Miami’s largely black Overtown neighborhood. The construction of a single highway cloverleaf resulted in 20 square blocks being demolished, displacing over 10,000 people in that community. The I-95 comprised unconnected segments between 1957 and 1965 through the densest urban areas in a deliberate effort to prevent premature suburbanization and to revitalize the downtown core. The I-71 cuts downtown Cincinnati off from its waterfront and a massive freeway interchange forced the destruction of dozens of blocks west of downtown. Freeway construction transformed Detroit between 1951 and 2010. Previously, its downtown had been surrounded by a high-density street grid. Today, it’s totally encircled by freeways. Rochester is one of many cities opting to undertake freeway removal projects. As the dotted line above shows, the “moat” surrounding downtown is slowly being removed. The city used reclaimed land from the Inner Loop freeway to construct three mixed-use developments that include below-market-rate units.
The Future of Urban Living: Do Highways Matter?
A new era of living is reconsidering the impacts of these highways on urban centers. As property values rise and existing housing stock is pressured, there are growing concerns over the environmental impacts of suburban life. As a result, urban planners and residents are looking to revitalize city cores and re-purpose land occupied by burdensome slabs of highway concrete.
Since 1987, there have been more than 20 urban highway segments removed from downtown cores, neighborhoods and waterfronts, mostly in North America. The pace of removals has picked up significantly and an additional 10 highways are now planned for removal in the United States.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, American cities have seen their traffic plummet. Rush-hour trips into cities are taking nearly half the time while some are not even commuting at all.
While this situation is likely temporary, it is offering a moment for reflection of how cities operate and whether the car should be at the center of urban planning.
*Hat tip to Shane Hampton, whose 60 Years of Urban Change compilation served as inspiration for this article. Visit that page for many more examples of highway impact on cities.
on
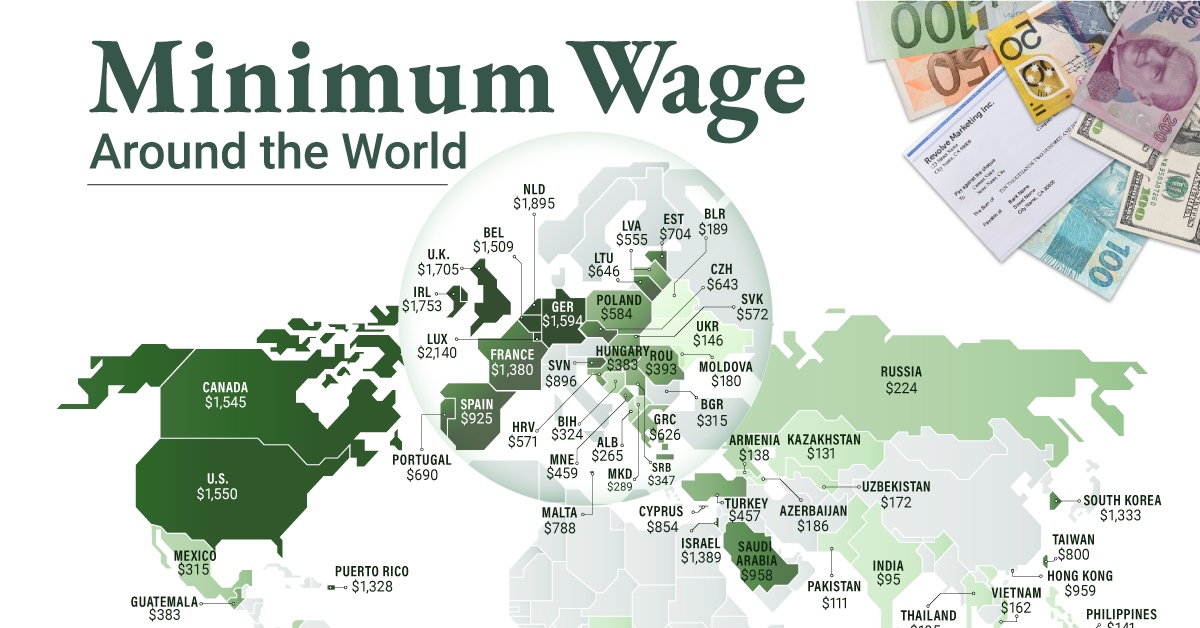
To see how the minimum wage differs around the world, we’ve visualized data from Picodi, which includes values for 67 countries as of January 2023.
Monthly Minimum Wage, by Country
The following table includes all of the data used in this infographic. Each value represents the monthly minimum wage a full-time worker would receive in each country. Picodi states that these figures are net of taxes and have been converted to USD. Generally speaking, developed countries have a higher cost of living, and thus require a higher minimum wage. Two outliers in this dataset are Argentina and Turkey, which have increased their minimum wages by 100% or more from January 2022 levels. Turkey is suffering from an ongoing currency crisis, with the lira losing over 40% of its value in 2021. Prices of basic goods have increased considerably as the Turkish lira continues to plummet. In fact, a 2022 survey found that 70% of people in Turkey were struggling to pay for food. Argentina, South America’s second-biggest economy, is also suffering from very high inflation. In response, the country announced three minimum wage increases throughout 2022.
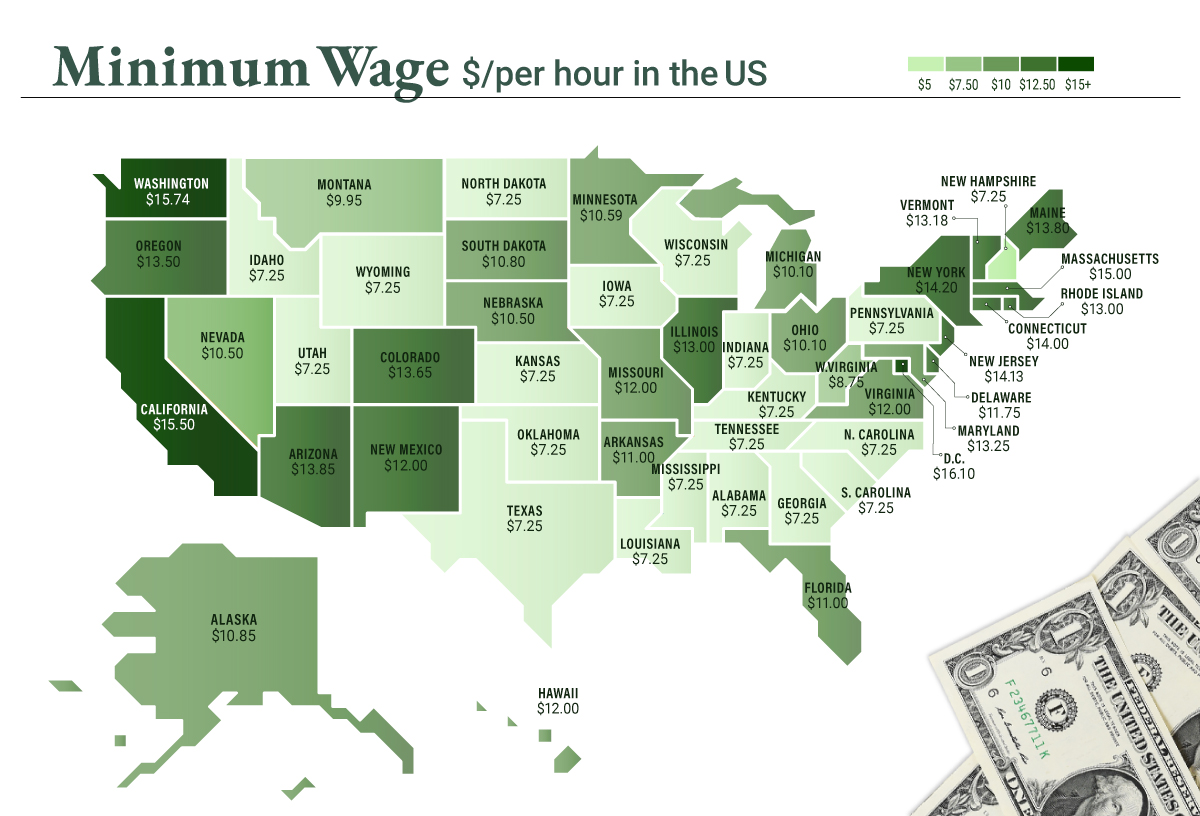
Minimum Wage in the U.S.
Within the U.S., minimum wage varies significantly by state. We’ve visualized each state’s basic minimum rate (hourly) using January 2023 data from the U.S. Department of Labor.
2023-03-17 Update: This map was updated to fix several incorrect values. We apologize for any confusion this may have caused. America’s federal minimum wage has remained unchanged since 2009 at $7.25 per hour. Each state is allowed to set their own minimum wage, as long as it’s higher than the federal minimum. In states that do not set their own minimum, the federal minimum applies. If we assume someone works 40 hours a week, the federal minimum wage of $7.25 translates to an annual figure of just $15,080 before taxes. California’s minimum wage of $15.50 translates to $32,240 before taxes. For further perspective, check out our 2022 infographic on the salary needed to buy a home across 50 U.S. cities.