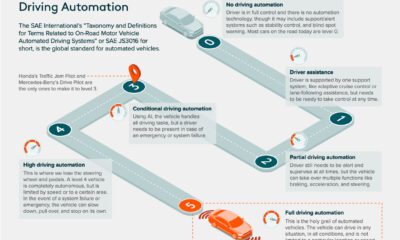
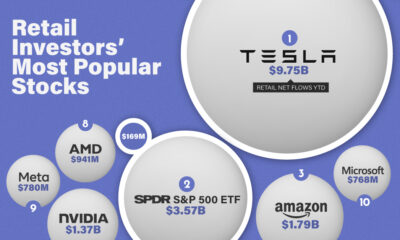
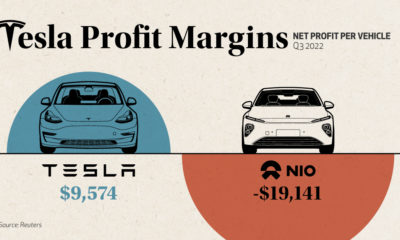
The vast amount of options available makes it increasingly difficult for brands to build meaningful emotional connections with them—but for the brands that do, the payoff can be huge. Today’s graphic pulls data from MBLM’s 2020 Brand Intimacy Report and visualizes the top 10 brands that different generations connect with the most.
Can Emotion Be Measured?
Brands that tap into consumers’ emotions can establish higher levels of trust. This in turn creates a culture of loyalty that could ensure a unique standing in the market and long-term growth. In fact, intimate brands that have a strong emotional bond with their consumers tend to outperform top companies listed on the S&P 500 and Fortune 500 in both revenue and profit. To measure how brands emotionally connect with consumers, MBLM looked at four key factors:
Users: The existing relationship between a brand and a consumer Emotional Connection: The degree of positive feelings the user has for a brand, and the extent to which their personal values align with the brand’s values Archetype: The six markers that are present among intimate brands, which include fulfillment, identity, enhancement, ritual, nostalgia, and indulgence Stage: The degree of intensity in the relationship across three phases: sharing, bonding, and fusing Intimacy Score: Based on these four components, a score is assigned, ranging from 0-100
The total score also reveals which brands rank the highest across different age groups. While there are some commonalities across each generation, can brands be all things to all people?
The Chosen One
Ranked: Top Brands by Generation
Gen Z and Millennials (18-34)
Sony-owned PlayStation holds the title for the most intimate brand among Millennials, climbing up from the 8th spot in 2019. Impressively, more than 50% of Millennials have an emotional connection to the brand, with men having a particularly strong affinity for it. Having recently celebrated its 25th anniversary, the gaming brand’s success has been fueled by the increasing popularity of multiplayer and professional gaming, as well as new product innovation—with five of the ten best selling consoles owned by PlayStation. Interestingly, when Gen Z (18-24) are singled out, Microsoft-owned Xbox ranks as #1, increasing its score to 73.5 in 2020 from 49.7 in 2018.
Gen X (35-54)
As the generational middle child, Gen X did not grow up with the same access to technology. However, their tech adoption is almost on par with Millennials, with similar adoption rates across tablet and smartphone ownership. It is no surprise therefore, that Apple has captured the hearts of this generation, sitting proudly in first place. When the iPhone launched in 2007, this group was between 22-41 years old, so they have likely been loyal followers of the tech brand since its earlier days.
Baby Boomers (55-64)
Controlling almost 70% of disposable income in the U.S., Baby Boomers are arguably the most influential of all consumer groups. This generation dominates almost 50% of consumer packaged goods (CPG) sales in the U.S.—which likely explains why the rest of their top brands are more traditional household names, such as Macy’s, Hershey’s, and Kellogg’s. It is also clear from the ranking that this group values brands with nostalgic qualities, as well as the ability to provide them with moments of indulgence.
The Changing Brand Landscape
The brand and consumer relationship has shifted with the ages, but each generation’s unique value system has remained the most important piece of the puzzle. It is worth noting that none of the Baby Boomer’s favorite brands appear in the ranking for those aged 18-24 (Gen Z). Are the preferences of younger generations signalling a cultural shift, in which we place more value on distraction rather than satisfaction? Note: The 2020 Brand Intimacy Report covers an age range of 18-64. The way that the ranking is structured makes it difficult to reflect conventional demographic groups (e.g. Gen Z, the Silent Generation etc.) on Even while political regimes across these countries have changed over time, they’ve largely followed a few different types of governance. Today, every country can ultimately be classified into just nine broad forms of government systems. This map by Truman Du uses information from Wikipedia to map the government systems that rule the world today.
Countries By Type of Government
It’s important to note that this map charts government systems according to each country’s legal framework. Many countries have constitutions stating their de jure or legally recognized system of government, but their de facto or realized form of governance may be quite different. Here is a list of the stated government system of UN member states and observers as of January 2023: Let’s take a closer look at some of these systems.
Monarchies
Brought back into the spotlight after the death of Queen Elizabeth II of England in September 2022, this form of government has a single ruler. They carry titles from king and queen to sultan or emperor, and their government systems can be further divided into three modern types: constitutional, semi-constitutional, and absolute. A constitutional monarchy sees the monarch act as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, giving them little to no real power. For example, King Charles III is the head of 15 Commonwealth nations including Canada and Australia. However, each has their own head of government. On the other hand, a semi-constitutional monarchy lets the monarch or ruling royal family retain substantial political powers, as is the case in Jordan and Morocco. However, their monarchs still rule the country according to a democratic constitution and in concert with other institutions. Finally, an absolute monarchy is most like the monarchies of old, where the ruler has full power over governance, with modern examples including Saudi Arabia and Vatican City.
Republics
Unlike monarchies, the people hold the power in a republic government system, directly electing representatives to form government. Again, there are multiple types of modern republic governments: presidential, semi-presidential, and parliamentary. The presidential republic could be considered a direct progression from monarchies. This system has a strong and independent chief executive with extensive powers when it comes to domestic affairs and foreign policy. An example of this is the United States, where the President is both the head of state and the head of government. In a semi-presidential republic, the president is the head of state and has some executive powers that are independent of the legislature. However, the prime minister (or chancellor or equivalent title) is the head of government, responsible to the legislature along with the cabinet. Russia is a classic example of this type of government. The last type of republic system is parliamentary. In this system, the president is a figurehead, while the head of government holds real power and is validated by and accountable to the parliament. This type of system can be seen in Germany, Italy, and India and is akin to constitutional monarchies. It’s also important to point out that some parliamentary republic systems operate slightly differently. For example in South Africa, the president is both the head of state and government, but is elected directly by the legislature. This leaves them (and their ministries) potentially subject to parliamentary confidence.
One-Party State
Many of the systems above involve multiple political parties vying to rule and govern their respective countries. In a one-party state, also called a single-party state or single-party system, only one political party has the right to form government. All other political parties are either outlawed or only allowed limited participation in elections. In this system, a country’s head of state and head of government can be executive or ceremonial but political power is constitutionally linked to a single political movement. China is the most well-known example of this government system, with the General Secretary of the Communist Party of China ruling as the de facto leader since 1989.
Provisional
The final form of government is a provisional government formed as an interim or transitional government. In this system, an emergency governmental body is created to manage political transitions after the collapse of a government, or when a new state is formed. Often these evolve into fully constitutionalized systems, but sometimes they hold power for longer than expected. Some examples of countries that are considered provisional include Libya, Burkina Faso, and Chad.